Arterial Treatments
Carotid Endarterectomy
Carotid Endarterectomy with Patch Angioplasty is a surgical procedure to treat carotid artery stenosis caused by plaque buildup. The plaque is carefully removed from the artery to restore normal blood flow to the brain, significantly reducing the risk of stroke. To reinforce and widen the artery, a patch made from bovine pericardium is sewn into place. This durable and biocompatible material minimizes the risk of restenosis and enhances long-term outcomes. The procedure is typically performed under general anesthesia and is an effective treatment for patients with significant carotid artery narrowing.

Diabetic Foot Care
Diabetic Foot Care focuses on preventing and managing complications such as ulcers, infections, and poor healing caused by diabetes, with an emphasis on vascular assessment and treatment. We provide comprehensive evaluations to assess blood flow and identify circulation issues that may impair healing. Our team specializes in advanced vascular interventions and wound care to restore proper circulation, promote healing, and prevent further complications. Our goal is to ensure optimal foot health and reduce the risk of serious outcomes for diabetic patients.
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Open Repair
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (AAA) Open Repair is a surgical procedure to treat an aneurysm—a weakened, bulging area—in the abdominal aorta. During the procedure, the surgeon makes an incision in the abdomen to access the aneurysm, removes the weakened section, and replaces it with a durable synthetic graft. This graft is sewn into place to restore the aorta’s normal blood flow and prevent rupture. Open repair is typically recommended for large or symptomatic aneurysms and provides a durable, long-term solution. The procedure is performed under general anesthesia, and recovery usually involves a hospital stay followed by several weeks of recuperation.
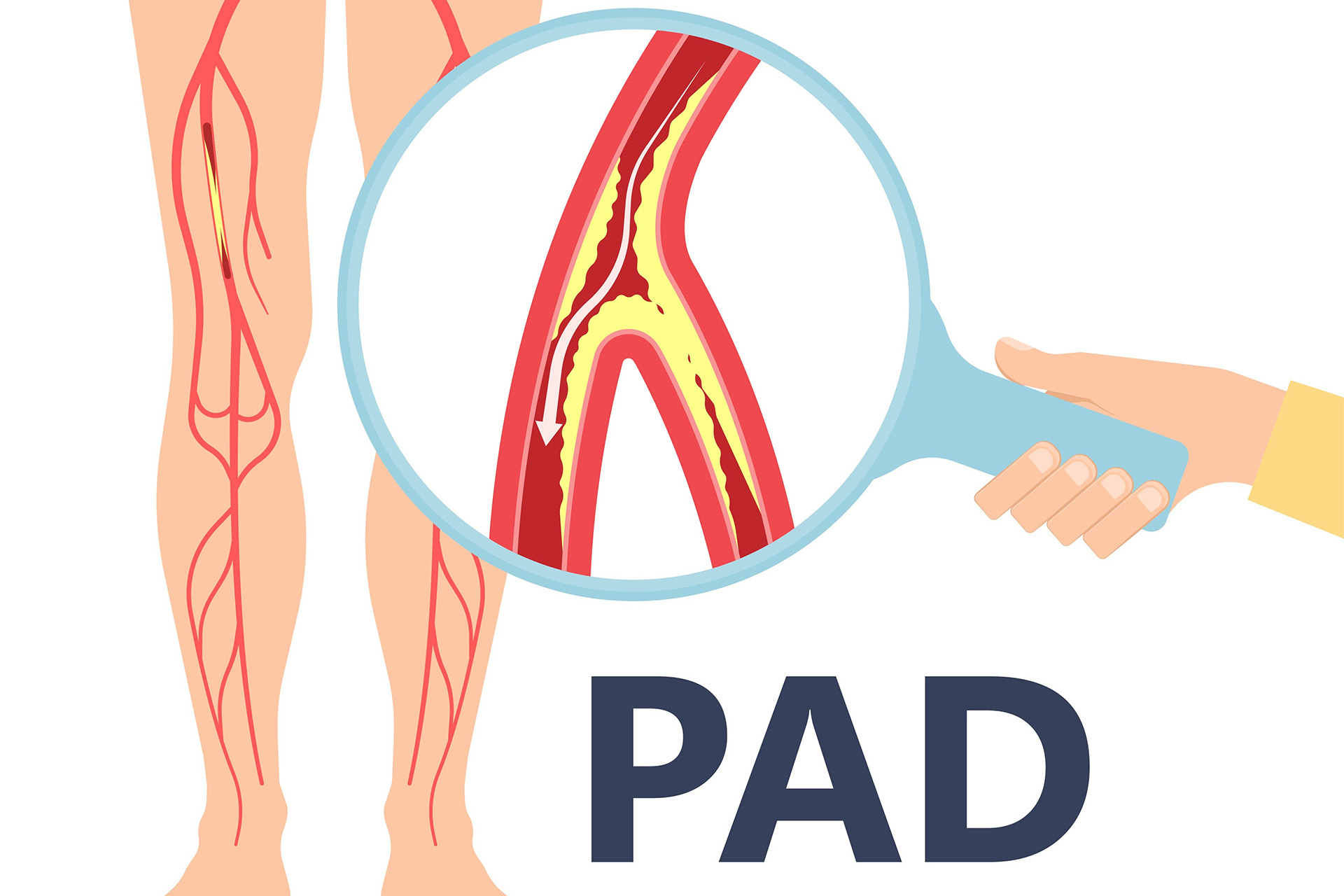
Peripheral Arterial Disease
Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) is a condition caused by narrowed or blocked arteries that reduce blood flow to the limbs, typically the legs. It is commonly associated with atherosclerosis, where plaque buildup restricts circulation. PAD can cause symptoms such as leg pain while walking (claudication), numbness, or non-healing wounds. If untreated, it may lead to severe complications like critical limb ischemia or amputation. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to restore circulation, relieve symptoms, and prevent further progression.
Surgical Bypass
Surgical Bypass is a procedure used to restore blood flow in arteries blocked or narrowed by conditions such as peripheral arterial disease (PAD). The surgeon creates a detour around the affected artery by using a graft, which can be made from the patient’s vein or synthetic material. This new pathway allows blood to bypass the blockage, improving circulation to the affected limb or organ. Surgical bypass is often recommended for severe cases where minimally invasive treatments are not suitable, providing effective, long-term relief of symptoms and preventing complications like tissue damage or limb loss.

Arterial-Venous Access Creation
Arterial-Venous Access Creation is a surgical procedure performed to establish a connection between an artery and a vein, typically in the forearm or upper arm. This procedure, often used for dialysis patients, involves creating a fistula (direct connection) or graft (using a synthetic tube) to provide a durable site for high-volume blood flow. The enhanced blood flow enables efficient dialysis while minimizing complications. The procedure is typically performed under local anesthesia and is crucial for patients with chronic kidney disease requiring hemodialysis.
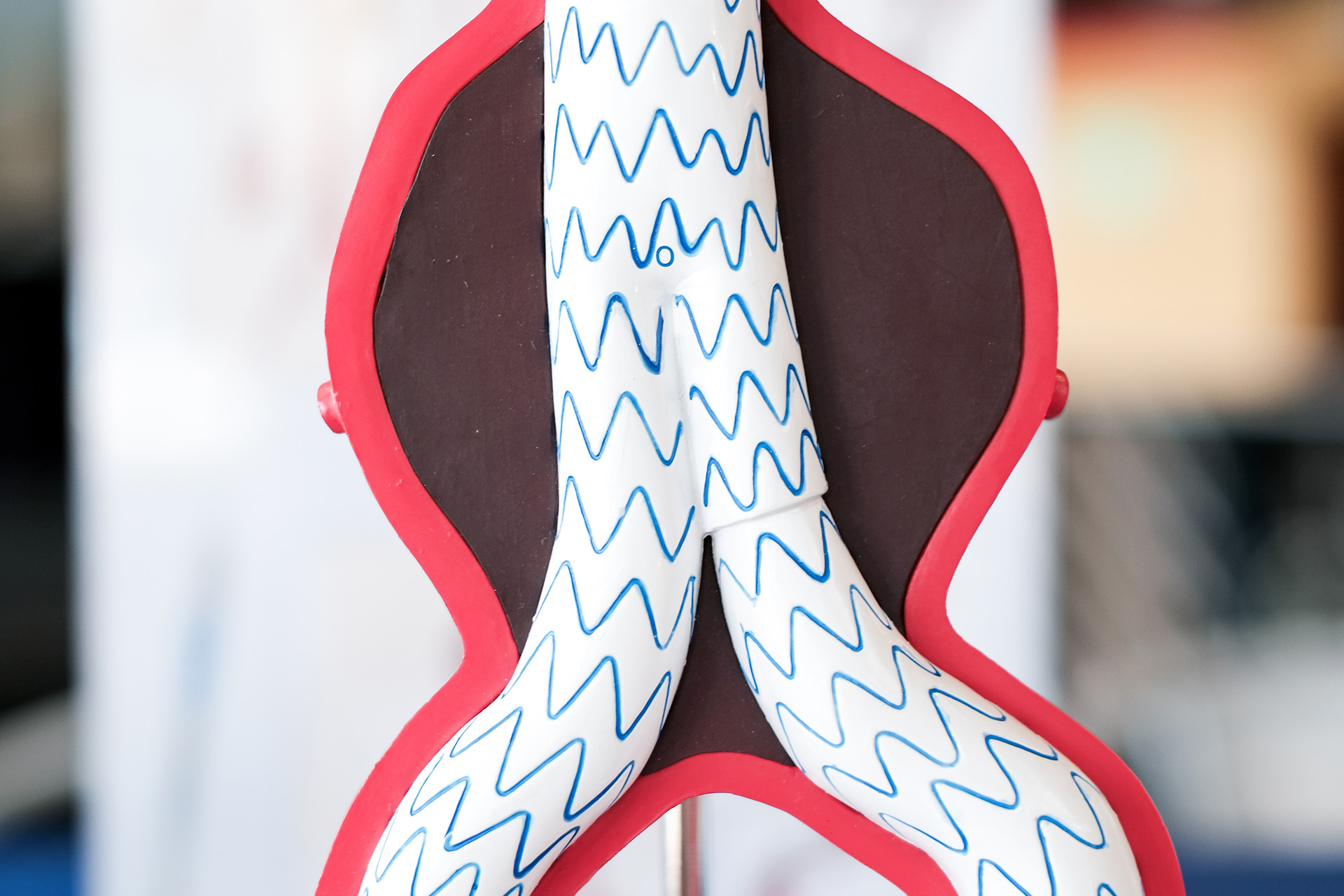

Endovascular Repair of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
AAA EVAR (Endovascular Aneurysm Repair for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm) is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat an aneurysm in the abdominal aorta. Through small incisions or punctures in the groin, a stent graft is guided to the aneurysm using advanced imaging. The stent graft seals off the aneurysm, reinforcing the aortic wall and redirecting blood flow to prevent rupture. Typically performed under general anesthesia, AAA EVAR offers faster recovery, less pain, and fewer complications in the early post-operative period compared to open surgery, making it a preferred treatment option for patients with suitable anatomy and those who are suboptimal candidates for open surgery.

Temporal Artery Biopsy
Bilateral Temporal Artery Biopsy is a diagnostic procedure performed to evaluate for giant cell arteritis (GCA), an inflammatory condition affecting the temporal arteries. The procedure involves taking small tissue samples from both temporal arteries through small incisions near the temples. These samples are then examined under a microscope for signs of inflammation, such as giant cells and vessel wall thickening. Bilateral biopsies are often performed to increase diagnostic accuracy, as GCA may affect one side more than the other. The procedure is typically done under local anesthesia in an outpatient setting, with minimal recovery time and low risk of complications.
About Us
Newmarket Clinic
Newmarket, ON
L3Y 9A2
Tel: (289) 903-1000
Fax: (289) 663-0999
Markham Clinic
Markham, ON
L3P 7M7
Tel: (289) 903-1000
Fax: (289) 663-0999


